Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), symptoms
There are two types of behavioral problems that can be identified in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- Inattentiveness (difficulty in focusing and concentrating)
- Hyperactivity and impulsiveness
Although ADHD can affect many people, not all ADHD sufferers fall under either of these two categories. As an example, approximately 2 to 3 percent of people with this condition have trouble concentrating and focusing, however, they are not affected by hyperactivity or impulsiveness.
Attention deficit disorder (ADD) is another name for ADHD. ADD may go unnoticed at times because symptoms are less obvious.
ADHD is more common in boys than it is in girls. ADHD symptoms are more common in boys than in girls. Girls are more likely only to display symptoms like inattention and less likely to exhibit disruptive behavior that can make ADHD symptoms more apparent. Girls with ADHD might not be diagnosed immediately.
Children and teens are at risk
ADHD symptoms in teenagers and children are well-defined and usually present before age 6. They can occur in multiple situations, including at home and school.
Sometimes children may exhibit symptoms of hyperactivity, inattention and impulsiveness. Other times they might display symptoms of only one of these behaviours.
Inattentiveness (difficulty in concentrating and focusing).
Inattentiveness is characterized by the following:
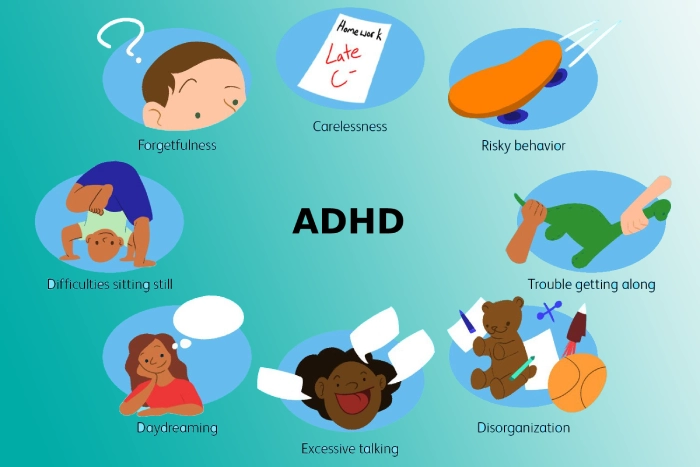
- Being easily distracted and having a limited attention span
- Making careless errors – such as in schoolwork
- Getting lost or forgetful
- Being unable to adhere to tedious or time-consuming tasks
- Appearing to be incapable of listening to or completing instructions
- Activities and tasks are constantly evolving
- Not being able to organize tasks
- Hyperactivity and impulsiveness
Hyperactivity and impulsiveness can be characterized by the following:
- Being unable to remain still in calm or quiet environments.
- Continually fidgeting.
- Being unable to focus on tasks.
- Excessive physical movement.
- Excessive talking.
- Being unable to wait for their turn.
- Acting without thinking.
- Interrupting conversations.
- There is little to no danger.
- These symptoms can lead to serious problems in a child’s life such as poor social interaction,
- Underachievement in school, and issues with discipline.
ADHD-related conditions in adolescents and children
While this is not always true, there are other conditions or signs that ADHD can cause in some children, including:
- Anxiety disorder is a condition that causes your child worry and to be anxious all the time. It may also cause physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeats, sweating, dizziness, and dizziness.
- Oppositional defiant Disorder (ODD), is a disorder that manifests in disruptive and negative behavior, especially towards parents or teachers.
- Conduct disorder, which is often characterized by a tendency to steal, fight, or harm people or animals.
- Sleep problems are when it is difficult to fall asleep at night or have irregular sleeping patterns.
- Autistic spectrum disorders (ASD) This affects social interaction and communication as well as behaviour.
- Dyspraxia is a condition that impairs physical coordination.
- Epilepsy is a condition in which the brain experiences repeated seizures or fits.
- Tourette’s syndrome is a condition that affects the nervous system and causes a mix of involuntary movements. and noises.
- Learning difficulties, such as dyslexia.
Adult Symptoms
ADHD symptoms are harder to identify in adults, due in large part to the lack of research on ADHD in adults.
ADHD is a developmental disorder, so specialists think that it can never develop in adults unless it appears during childhood. The symptoms in children and teens often persist into adulthood.
Adults can experience hyperactivity, inattention and impulsiveness in a different way than children. As adults age, hyperactivity tends decrease, and inattentiveness increases with the increased demands of adulthood.
ADHD symptoms in adults are often more subtle than those of childhood. Some specialists suggest the following list of ADHD symptoms in adults:
- Neglecting to pay attention to details and carelessness.
- Always start new tasks before you finish old ones.
- Poor organisational skills.
- Inability to focus on or prioritize.
- Frequently losing or misplacing items.
- Forgetfulness.
- Restlessness and edginess.
- Having trouble keeping quiet and speaking out of turn.
- Interrupting other people and blurting out their responses is a common tactic.
- Feelings of mood swings, irritability, and quick temper.
- Inability to manage stress.
- Extreme impatience.
- You take risks by engaging in dangerous activities.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder related conditions in adults
ADHD can also occur in adults, as with ADHD in children or teenagers. Depression is one of the most common condition, and adults may also have the following conditions:
- Personality disorders are conditions where an individual’s thinking, perception, feelings, and relationship to others is significantly different from the average person.
- Bipolar disorder is a condition that affects your mood and can swing from extreme to extreme.
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a condition that causes compulsive thinking and compulsive behaviour.
ADHD-related behavioural issues can also lead to problems in relationships and social interaction.